In the high-end mobile phone market, Samsung, Huawei, Xiaomi and other flagship phones adopt eMMC or UFS separate storage solutions, that is, CPU encapsulation and Mobile DRAM (including LPDDR2, LPDDR3, LPDDR4, LPDDR4X, etc.)pop package, because it can ensure the high quality of mobile communications. With the bottleneck of eMMC speeding up and the increase of UFS supply by Samsung and Toshiba, UFS has basically replaced eMMC as the standard of its flagship models such as Samsung, Huawei and Xiaomi.
The original UFS should be from the high-end mobile phone market to the low-end market to expand popularity, but because of the NAND Flash market in 2016, leading the eMMC and UFS prices soared, including eMMC highest cumulative increase of more than 60%, also widened gap of eMMC and UFS. Taking into account the cost factors, most of the low-end phones still use eMMC / eMCP mainstream storage solutions.
eMCP encapsulates mobile DRAM and eMMC. 2017 is not only the NAND Flash to be out of stock and price increases, mobile DRAM also faces the same problem, for handset manufacturers, the storage industry in a critical period of shortage, it is necessary to ensure the mobile phone shipped mobile DRAM but also to ensure eMMC supply, inventory control difficultly, eMCP naturally become the preferred solution for most low-end phones, and even OPPO R11s, VIVO X20 are also used eMCP solution.
The reasons for choosing the eMCP solution are as follows: First, eMCP has the advantage of high integration, including two chips, eMMC and mobile DRAM. It simplifies the circuit design of handset PCB and shortens the shipping cycle for terminal manufacturers. Second: For upstream OEMs, eMCP bundles eMMC and mobile DRAM two product lines, which will help increase shipments. Third: Considering the cost factor, the eMCP purchase cost is slightly lower than that of eMCP and LPDRAM, and the purchase risk is reduced during the period of stock-out and price hikes.
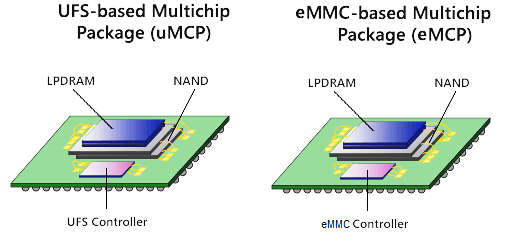
uMCP (UFS + LPDDR) and eMCP (eMMC + LPDDR) structures
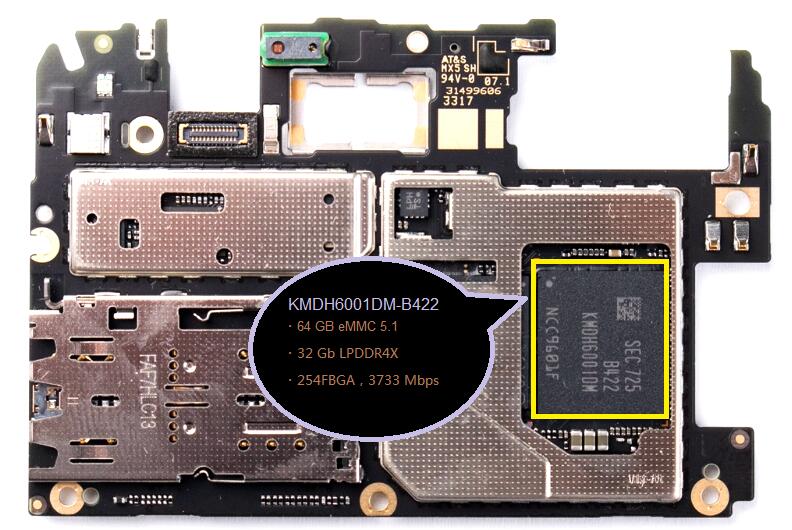
ViVO X20 solution
|